Take Advantage of the Federal Battery Rebate & Maximise Your Savings Today
Take Advantage of the Federal Battery Rebate & Maximise Your Savings Today
Posted 4 Dec
Want the latest in energy, solar, and savings?Subscribe to our newsletter – we don’t spam!
When we make coffee, wash our clothes, or turn the oven on, we rarely stop to think about the electricity powering it, let alone the marketplace of where this electricity is bought and sold. Australia's electricity system is a complex and evolving network that provides east-Australia with electricity, but how does it work?
The National Electricity Market (NEM) is a wholesale electricity market that participants like retailers can buy and sell energy across the east states of Australia.
Since 1988, the National Electricity Market, otherwise known as 'the NEM' is responsible for electrically interconnecting Australian states NSW, ACT, QLD, VIC, SA, and TAS.
As it is difficult to store electricity, they distribute the electricity into the markets as a “pool”. The “pool” or spot market is where supply and demand of power is instantly complimented through a centralised process.
Overall, the NEM is an extremely important part of ensuring electrical grid balance and distribution throughout the East Coast of Australia.
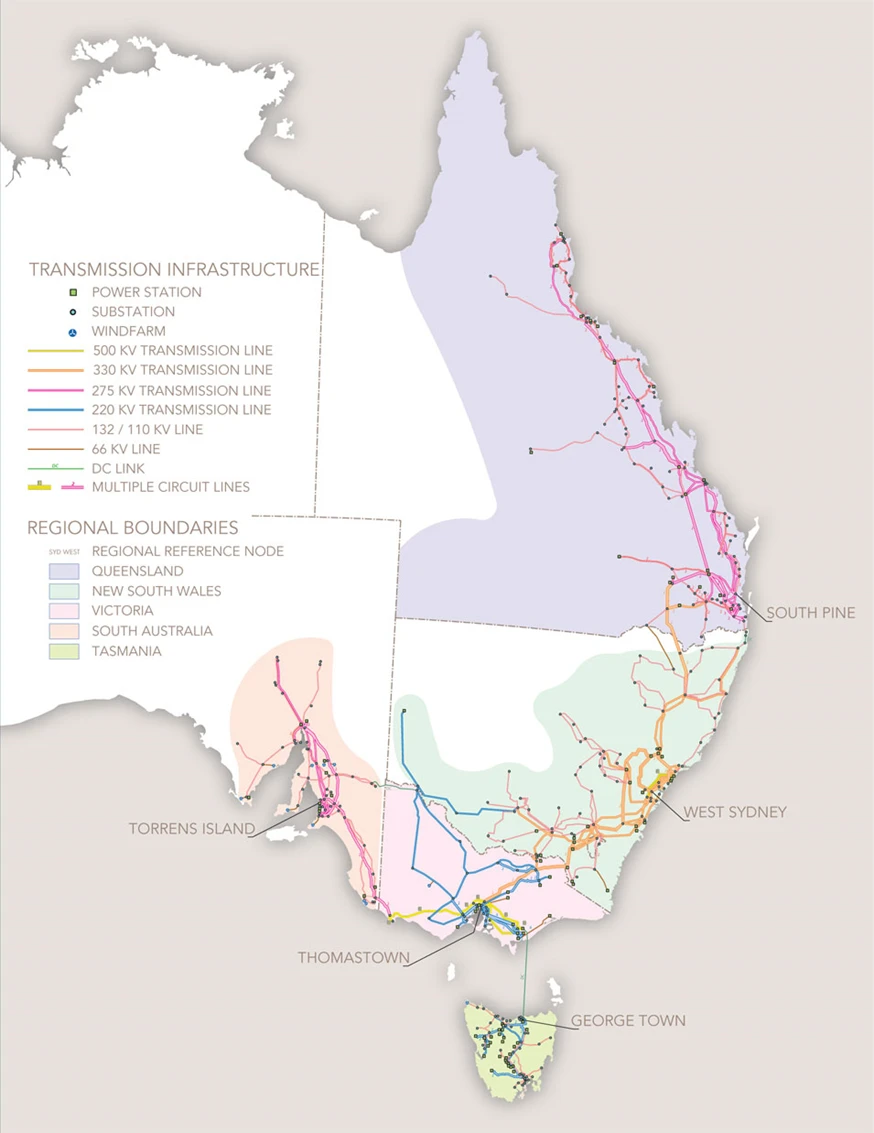
Courtesy of Australian Energy Market Operator
In the nature of electricity, supply always needs to be balanced with demand. At times of imbalance, where supply or demand outstrips the other, it causes grid voltage drops as electricity always needs somewhere to go.
In times of too little energy generation as well as strong demand causes the grid to drop voltage, and the reverse to cause a rise in the grid's voltage which has the ability to damage appliances.
The NEM has interconnected QLD, NSW, VIC, SA, and TAS, and is responsible for distributing electricity to balance grid supply and demand in real-time, for almost 10 million residential, commercial, and industrial energy users.
Even with supercharged battery adoption throughout Australia, electricity can't be easily stored in large amounts, which means that the electricity needs to go somewhere.
To balance supply and demand at all times, the NEM manages generation like coal, gas, hydro, wind, and solar, retailers, 40,000km of transmission lines, and the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO).
To ensure the grid remains stable and both supply and demand are balanced, the AEMO manages the NEM in real time, where they forecast consumption, monitor system health and security, and coordinate distribution.
Once a retailer like Origin, AGL or Energy Australia buys electricity from the NEM, they sell it to homes and businesses which is transported through high-voltage electricity lines from power stations. Retailers are obligated to supply us with energy at a fixed price, in-which they absorb any market price fluctuations.
What does AEMO mean? The organisation which controls the NEM is the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO). The AEMO receives its operating rules and authority from the Australian Energy Market Commission (AEMC), which in turn receives its overarching authority and policy from the state governments in which the NEM operates.


The National Electricity Market prices are dynamic in nature where they vary depending on elements like location, time, fluctuations in demand, mix of various energy sources, transmission, and fuel expenses.
In peak consumption periods where renewable energy generation is low, the energy prices rise. Abundant renewable energy generation
like solar and battery helps reduce wholesale prices.
There are 2 elements that determine the price of the wholesale electricity: the offers submitted by generators and the level of energy demand at any given time.
The spot price is determined every 5-minutes, which is averaged over a 30-minute period to calculate the half-hourly spot price for each region.
Depending on the supply and demand balance, electricity prices in the NEM are volatile and can fluctuate throughout daily, monthly, or even seasonal periods. Other elements like weather events, generation, and supply shortages can negatively impact prices.
The NEMs minimum and maximum wholesale electricity prices range from the market floor of $1,000 per MWh to a market cap of $14,700 per MWh.
Even though the National Electricity Market is such a large and complex system, we are still able to harness data that shows us statistics from 2024 that shows us what sources of generation our NEM distributed.
In a report by the Australian Energy Regulator (AER), it shows us the state of the energy market at the end of 2024 (data from 2025 will still be processing). Highlighting 2024's sources of generation statistics, it shows us each generation capacity by fuel source.
31,594 MW
16,389 MW
4,690 MW
12,760 MW
10,799 MW
7,609 MW
2,455 MW
649 MW
What does DER mean? Distributed Energy Resources (DER) refer to consumer-owned appliances that generate or store electricity, or can actively manage demand.
Examples of DER include rooftop solar (PV), wind generation, battery storage, hot water systems, smart appliances, and electric vehicles.
Distributed Energy Resources (DER) fall into the efficiency logic of using the energy close to the point of where it was generated. Home solar is a DER, which generates solar power to be consumed - the ultimate efficiency.
With solar battery storage adoption going crazy with the federal rebate, it is providing value to homes and businesses wanting to store excess solar energy.
As more properties adopt solar and battery throughout Australia, the result would be a decrease in high peak demand periods on a large-scale, as well as minimising large price fluctuations within the National Electricity Market.

Other than being an Australian-made marvel of what our engineers can do, the National Electricity Market (NEM) is very important in the way we generate, distribute, and consume power. From making coffees to keeping things cool, the NEM will continue to power the east side of Australia for a long time, but at least you now know how it works.
Compare Tesla Powerwall 3, Sungrow SBR & SBH, GoodWe ESA, Fronius Reserva, and BYD Battery-Box to find the best home battery for Australia.
Read moreExplore how Australia’s Q4 2025 solar and battery data highlights a major milestone: majority renewable contribution to daytime electricity demand.
Read moreHow rooftop solar helped NSW avoid blackouts during the 2026 heatwave, reducing grid stress & supporting record electricity demand across Newcastle.
Read moreRenewable News Articles
We've invested in becoming fully-licenced and qualified installers to ensure Newcastle homes and businesses
get the best systems and installations possible. We want to assist Newcastle's renewable energy revolution with quality systems.
Certified solar system installers near you.
Get CEC-Approved Battery Installations.
Fully-licenced electricians in Newcastle.
Convenient EV charging stations for properties.
Leave a Comment