NSW's Heatwave 2026: How Solar Helped Stabilise the Grid⚡
How rooftop solar helped NSW avoid blackouts during the 2026 heatwave, reducing grid stress and supporting record electricity demand across the state.
Read more
Tesla Powerwall 3 Rebate Now Available - Combine with Federal Subsidy Today
Posted 17 Nov
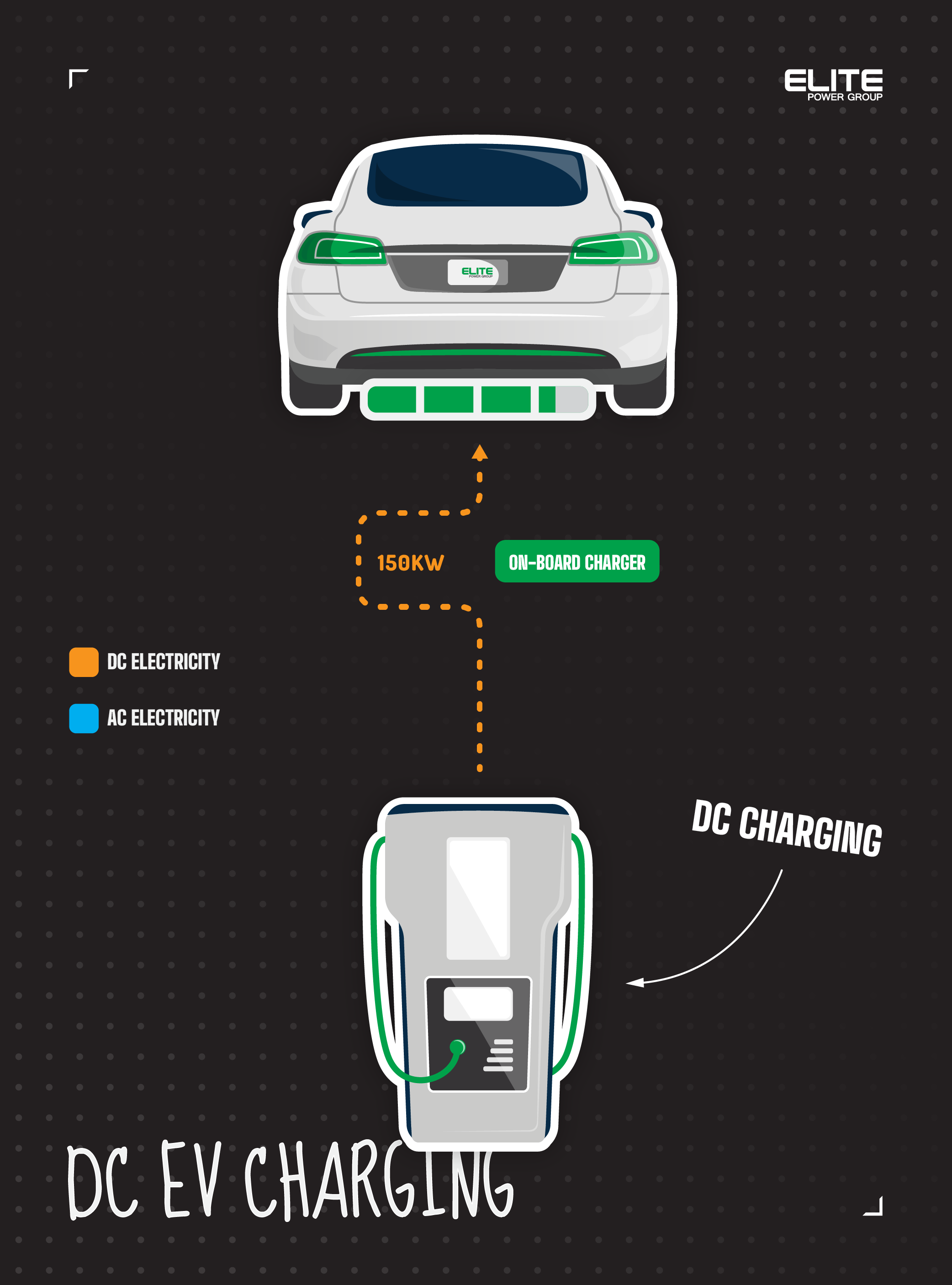
For those who want to, or already own an electric vehicle, you’ve probably heard ‘AC’ and ‘DC’ charging, but what does it mean? Explore the differences between AC and DC electric vehicle charging in Australia, the pros and cons, and how it affects the way you charge your EV.
AC (Alternating Current) charging is when the installed charger acts as an appliance, using the home’s AC power supply, which sends AC electricity to the EV where an onboard inverter is responsible for converting it to DC power for the battery.
DC EV charging on the other hand converts the grid-supplied AC electricity to DC in the charging station itself which goes directly to the EV’s battery for increased speeds, hence the size of DC fast chargers.
In Australia, all home and home appliances run on grid-supplied alternating current (AC) electricity. Most 7-22kW chargers are AC chargers, which send the AC electricity to the EV to charge.
How fast is AC Charging? AC charging consists of level 1 and 2 chargers, providing from 2.4kW in a standard home outlet, 7kW for single phase, and up to 22kW for three-phase properties using three-phase electric vehicle chargers like myenergi’s Zappi charger.
Whilst AC chargers can provide up to 22kW of charging, it’s important to note that your EVs built-in inverter (or ‘on-board charger’) may bottleneck charging speeds with specification limitations.
What does alternating current mean? AC simply refers to when the electrical current switches direction in a circuit, which is used for homes, appliances, and long-distance transmission.

An onboard charger or inverter is responsible for converting chargers’ AC electricity from the home or grid to DC electricity for the battery. The onboard charger is only required for AC chargers and can be a limitation to charging speeds depending on your EV model.
For example, the Tesla Model Y has an 11kW on-board charger which works well with Tesla Wall Connector which provides up to 11.5kW of AC charging power, but also means that a 22kW charger won’t be fully utilised as the inverter is capped at 11kW.
Is 11kW three-phase? As single-phase properties can only get 7kW, to achieve 11kW your property will need to be three phase.
Whilst DC also provides power to your EV, this time, the AC to DC conversion happens inside the charging unit, which inverts the AC into DC which can be sent straight into the EV battery bypassing the on-board charger and its limitations.
DC chargers can unlock much faster charging speeds, with some reaching 480kW of power. DC fast chargers (DCFC) are typically used in applications like public and fleet EV charging stations that require fast and rapid charging systems to recharge electric vehicles as quickly as possible.
Whilst DC EV chargers can be installed for homes, they are typically very expensive coming in to more than $10,000, accounting for the additional tech, and home infrastructure to support it.
What does direct current mean? As opposed to AC, direct current (DC) flows in one direction which you see mainly in phones, batteries, and solar panels.
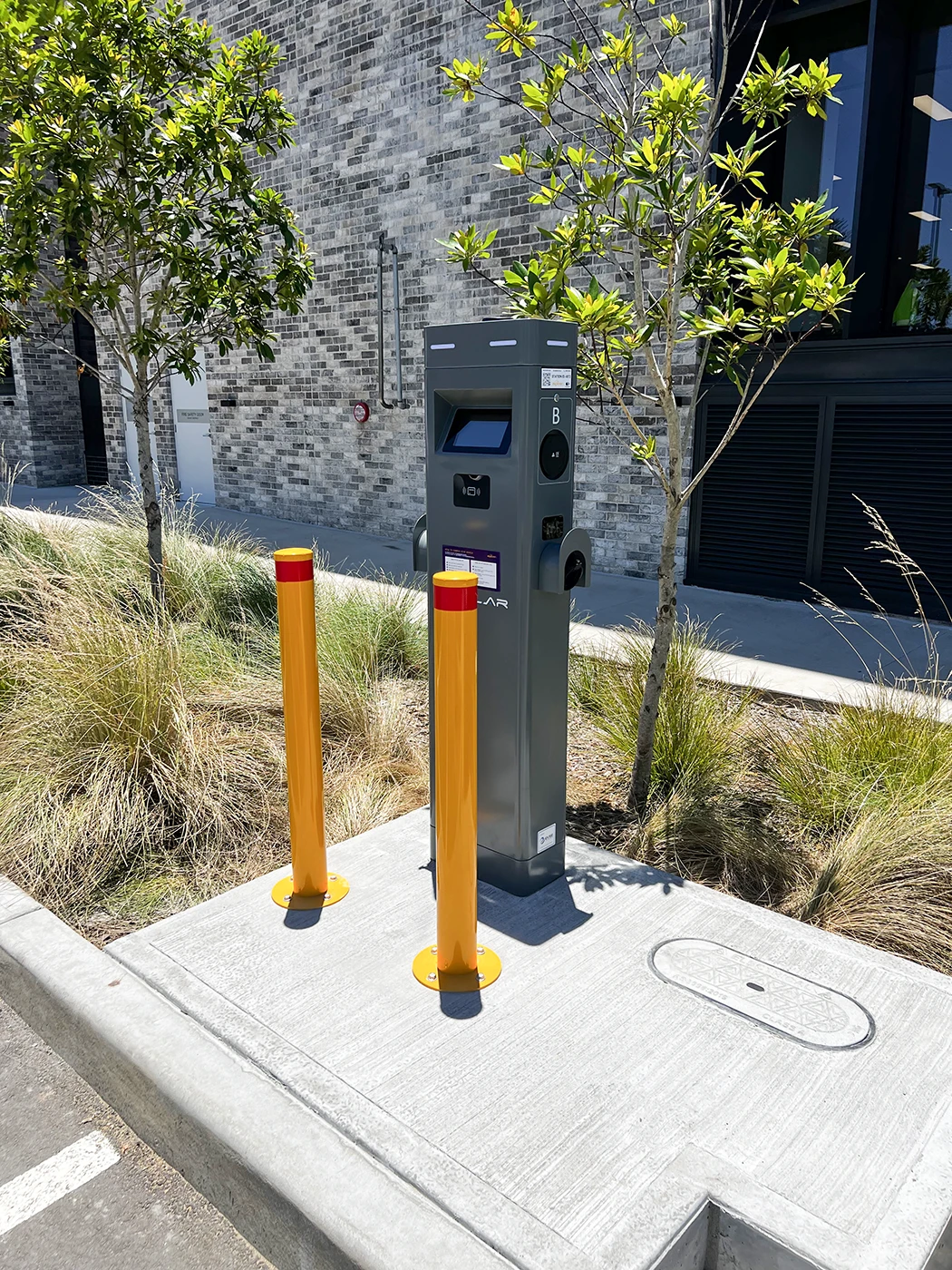
As installers of EV chargers across
Newcastle & the Hunter, our criteria for the best AC & DC electric vehicle chargers consist of reliability, quality, and
functionality. Using these, we highly recommend the following chargers as we think these are the best AC EV charger options for households
and businesses in Australia.

In most cases, a combination of both AC and DC charging will be sufficient in keeping your electric vehicle topped up. However, there may be situations where certain drivers have specific requirements that may alter recommendations.
For example, if you’re someone who works all day, and then parks in their garage at night and repeats the next day, an AC EV charger may be preferential as it fits directly into your lifestyle.
On the other hand, if you’re someone who is regularly on the road and needs constant 0-80% charges as quickly as possible, relying on public DC chargers may be the better choice.
Most EV owners will opt for both solutions, with AC charging being much more convenient at home, and relying on public EV charging stations for quick charges throughout the week.
Because both AC and DC chargers technically end up charging the battery with DC electricity with either the DC charger or on-board charger supply the DC electricity, it shows us that AC and DC don’t directly affect the battery’s lifespan.
The battery lifespan is determined by the speed of the charging. AC chargers max out at 22kW which is a good speed for gradual and consistent charging, whilst DC chargers can reach up to 480kW. High-powered chargers provide generate more heat and cell stress, but with modern charging management technology, the difference is minimal.
During the process of fast charging, the curve is set to optimise battery performance and prolong battery health to ensure longevity.

Courtesy of Erik Mclean on Pexels.
The main difference of AC and DC charging really comes down to how fast and the way your EV is charged. The pros of AC charging are convenience, cost effectiveness, and how it's designed for routine. AC's cons are slower and less efficient charging compared to DC.
The pros of DC charging consists of higher speeds of power (up to more than 400kW) and suitability for public charging stations, with its
cons being more expensive and requiring upgraded electrical infrastructure.
Features |
AC EV Charging |
DC EV Charging |
| Current Type |
Alternating Current |
Direct Current |
| Conversion |
Uses on-board EV inverter |
Inside the DC charger |
| Typical Power (kW) |
2.4kW – 22kW (slower) |
25kW – 480kW (faster) |
| Designed for |
Designed for homes, workplace, and public charging – daily and overnight charging. |
For public charging stations, and commercial fleet charging, for rapid recharges and road trips. |
| Connector Types |
Type 2 (AC) |
CCS2 (DC) |
Whilst both AC and DC chargers can generate heat, they both require various methods of cooling to accommodate their power output.
AC electric vehicle chargers generate heat like other electronics, however, they are designed to have adequate cooling by implementing natural convection or passive cooling. Fans aren’t required because the charger is not inverting the AC to DC which would generate heat from conversion power loss.
DC EV charging stations require strong cooling methods to deal with the high-power transfer and inversions that happen inside the charger unit. Delivering hundreds of kW of power at any given time, DC superchargers require heat management like liquid cooling in the charger, and sometimes in the charging cable itself.
It’s not only important operationally to keep each charging station cool, but it’s also important for ensuring safety and protection of the
property, charger, and customer.
Whilst they achieve the same purpose, both AC and DC electric vehicle chargers are designed for specific purposes to help keep local electric vehicles on the road.
With the uptake in electric vehicles in Australia, the demand for sufficient chargers and infrastructure becomes more and more important. In
the future, both AC and DC electric vehicle chargers will play a major role in our energy management and powering transportation.
How rooftop solar helped NSW avoid blackouts during the 2026 heatwave, reducing grid stress and supporting record electricity demand across the state.
Explore Elite Power Group's solar and battery installation statistics for 2025, and how we performed over this year of operation in Newcastle and Maitland.
Explore the differences between peak shaving and load shifting and how it can maximise solar & battery, reduce your bills and grid reliance in Australia.
Explore the difference between solar inverter types like grid-tied, hybrid, microinverters, and off-grid inverters for solar and battery systems in Australia.
Explore Australia's first CEC-approved bidirectional and vehicle-to-grid capable electric vehicle, the V2Grid Numbat, a 6.2kW V2G/H charger now ready.
Explore how battery nominal & useable energy capacity is different to power output, and learn about state of charge, depth of discharge, and cycles.
Renewable News Articles
Not only are we specialists in solar power, but we pride ourselves in being leading installers in battery
storage, as well as EV charging for homes and businesses. For solar and battery systems, we offer both on and off-grid solutions for a
range of applications.

Newcastle's leading solar installers, providing long-lasting residential and commercial rooftop solar systems.

Experts in both residential and commercial electric vehicle charging station installations from 7kW - 360kW+.

Specialists in off-grid solar and battery, helping properties never have to pay another electricity bill again.

With decades of electrical and industry experience, our fully-qualified & licensed electricians are here to help.

Maximise your solar generation with battery storage from reputable brands to accelerate return-on-investment.
Leave a Comment